Blog
JReserv: We finished the requirement phase
We are pleased to announce that we have completed the requirements phase of JReserv project. Here are the features that we will implement in the first version.
- Management:

- Resources Management
- Packages Management
- Prices and Availabilities Management
- Clients Managements
- Agents Managements
- Configuration Managements
- Services that would be offered to visitors:
- Resources Catalog and Packages
- Online Booking
1 Resources Management:
The system will allow the management of resources, allowing to Create, Read, Update y Delete (CRUD) them. The system must store relevant information about it including: title, description and images.
Also should allow to classify the resources in a flexible manner in order to be suitable for any business allowing the proper adaptation of the tool to any environment. A resource would be associated to a bookable category which will be associated with one or more than one category. At the same time, a category can be classified in other parents categories. For example, for a resource of a hotel called “101 room” could be associated to a bookable category called “Double Room”, which may be associated with the following categories “Caesar Hotel” to define that it belong to this hotel. At the same, this hotel may be associated with “Santa Fe” to identify to which city belongs.The category “Caesar Hotel” may be a children of another category called “Emperors Chain” to identify which chain owns the hotel while “Santa Fe” is the children of “Argentina” to determine to which country it belongs. As you can see this is very flexible and could be adapted to any business.
A bookable category may be associated to one or more addons. These addons can be purchased at the same time of the booking. For example, by booking a “Double Room” we would be able to add to our order a “Dinner Menu”. It is possible that the addons impact on the price of the reservation.
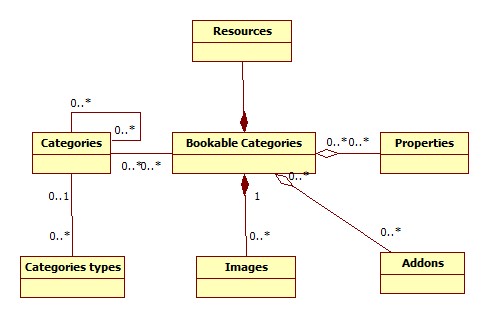
Picture 1: Entities associated with resources
Bookable categories and categories would also have associated properties that represents its characteristics. Having this information in a separate entity will allow to perform searches of resources and categories which have these characteristics in common. As an example, the resource “Double Room” could have assigned properties “Jacuzzi”, “Private Bath”, “Air Conditioning”. Then if you’re interested in making a reservation for a room with Jacuzzi you could make a filtering to obtain a list of all the rooms that have those features and then choose between them.
MySpaceID: Another way to login to a website without registration
What is MySpace?
If you have a profile of “Developer” on MySpace then you will be able to create applications. These can be of 2 types: internal or external. The first are developed to introduce into our profile iframes with our applications, the second type (which we are interested in remaining article) allow us to create ‘Lives App’ or external applications of MySpace in order to extract information from the API and use it on our websites. This tool is known as MySpaceID.
Implementation:
The first thing we must do is create an application on our MySpace account developers (must have prior permission to develop, this procedure takes about 48hs).
When we have access, go https://developer.myspace.com/community/ -> MyApps -> Create New MySpace Application and choose type.
In ‘external callback’ Enter the URL of our site and remember to save OAuth Consumer Key and OAuth Consumer Secret.
Once created the application must publish, we should see a sign: Status changed to [Live], if this happens we are able to use our site.
Facebook Connect: Login to a website without registration
What is Facebook Connect?
Facebook’s new product called Facebook Connect allows us to use the same login on multiple sites without the need to record us as a new user.
With this new service, we may also import all our contacts and our social network, with full profile, to the other sites included in the agreement.
The rough idea is to share the record of Facebook on other sites to avoid having to register each time.
How to Link to Facebook?
1. Create a Facebook application development: we must start by having a user, then enter the developers area https://www.facebook.com/developers/editapp.php to register a new application. We have to fill optional fields and CallBack URL with the URL of the site to which we link Facebook. Leave the other in default would be the right thing, then accept.
I recommend saving the API Key, because we use it in a moment.
2. File Connection: Now we return to our project. We can create a folder to save files in Facebook, or place them in the same root.
The first file you need to create is one that creates the connection to Facebook:
xd_receiver.htm
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
Creating mambots for Joomla 1.0.x
This article will explain how to create a mambot on Joomla 1.0.x (Plugins from Joomla 1.5). It is recommended to have knowledge of PHP and HTML to read this article.
What is a Mambots?
Mambots are the applications that intercept the contents (documents or items of components) before being published and displayed by the system, and add or alter information dynamically, thus completing the total content that will be delivered the end user’s browser. The Mambots can be called by special commands, or can be displayed by default for certain content / components.
Mambots are located in the directory /mambots. As the components and modules can be installed/uninstalled, configured and published from the backend of Joomla.
Triggers:
At present there are 5 factors (documented) to trigger a Mambots:
- onPrepareContent
- onSearch
- onInitEditor
- onGetEditorContents
- onEditorArea
Each event require a numer and parameters.
Example of a Mambot:
As modules, Mambots are composed of two core files. One is the .xml file that gives the configuration for the installation, and the other is .php file that allows us to codify what the mambots will do. Al the mambot files should start with “mos”.
